I was deploying my containers onto kubernetes through this article I wrote a while back. What happens if I want to change a bit of my code ? Would I have to locally rebuild the docker container and then push it to the docker container registry manually ? There had to be a better way.
Approach
- Enforce a ci/cd pipeline through Github Actions that automatically pushes code from the main branch to the docker container registry (e.g dockerhub or ghcr)
- Connect the uploaded container image to the Kubernetes Application.
Enforcing CI/CD
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (or Continuous Deployment). It is a software engineering practice designed to automate and streamline the process of building, testing, and releasing code.
GitHub Actions is a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) platform built directly into GitHub. It allows developers to automate workflows that build, test, and deploy code whenever certain events occur in a GitHub repository.
Github Actions mainly deals with events & actions in a workflow
eventsare anything that happen in or to your repository.actionsare the defined operations that should be done as a result of events being triggered.workflowis a sequence of events and actions that are configured for a specific purpose e.g publishing a container to a docker container registry
Prebuilt Workflows
Github Actions has many templates you can use to implement github actions for your use case. In this case, you can search for Publish Docker Container as below:
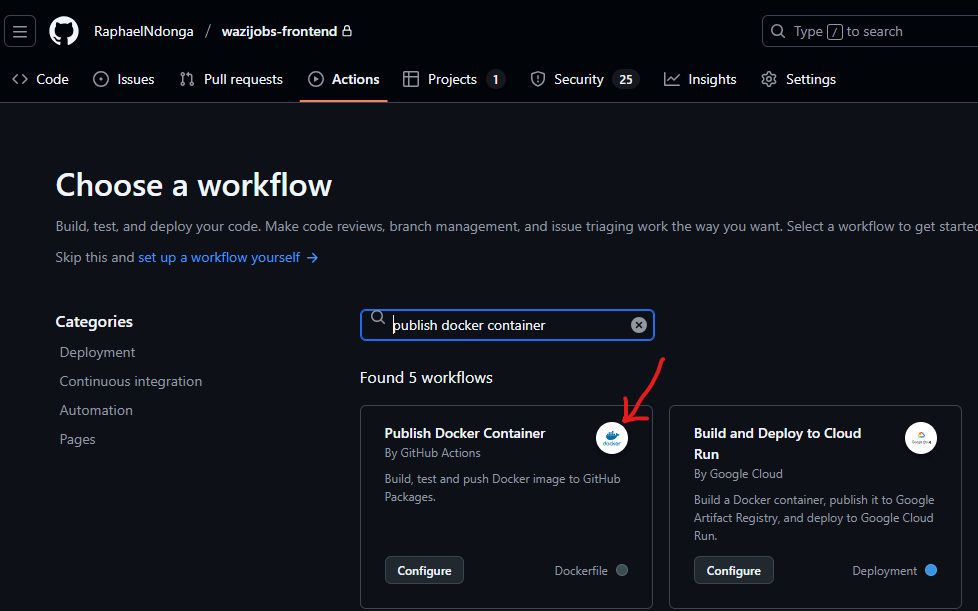
It adds a docker-publish.yml file under .github/workflows as below:
name: Docker
# Define the events using "on"
on:
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
# Publish semver (semantic versioning) tags as releases.
tags: [ 'v*.*.*' ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "main" ]
env:
# Use docker.io for Docker Hub if empty
REGISTRY: ghcr.io
# github.repository as <account>/<repo>
IMAGE_NAME: ${{ github.repository }}
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: read
packages: write
# This is used to complete the identity challenge
# with sigstore/fulcio when running outside of PRs.
id-token: write
# Define the actions using "steps"
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4
# Install the cosign tool except on PR
# https://github.com/sigstore/cosign-installer
- name: Install cosign
if: github.event_name != 'pull_request'
uses: sigstore/cosign-installer@59acb6260d9c0ba8f4a2f9d9b48431a222b68e20 #v3.5.0
with:
cosign-release: 'v2.2.4'
# Set up BuildKit Docker container builder to be able to build
# multi-platform images and export cache
# https://github.com/docker/setup-buildx-action
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@f95db51fddba0c2d1ec667646a06c2ce06100226 # v3.0.0
# Login against a Docker registry except on PR
# https://github.com/docker/login-action
#
- name: Log into registry ${{ env.REGISTRY }}
if: github.event_name != 'pull_request'
uses: docker/login-action@343f7c4344506bcbf9b4de18042ae17996df046d # v3.0.0
with:
registry: ${{ env.REGISTRY }}
username: ${{ github.actor }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
# Extract metadata (tags, labels) for Docker
# https://github.com/docker/metadata-action
- name: Extract Docker metadata
id: meta
uses: docker/metadata-action@96383f45573cb7f253c731d3b3ab81c87ef81934 # v5.0.0
with:
images: ${{ env.REGISTRY }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}
# Build and push Docker image with Buildx (don't push on PR)
# https://github.com/docker/build-push-action
- name: Build and push Docker image
id: build-and-push
uses: docker/build-push-action@0565240e2d4ab88bba5387d719585280857ece09 # v5.0.0
with:
context: .
push: ${{ github.event_name != 'pull_request' }}
tags: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.tags }}
labels: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.labels }}
cache-from: type=gha
cache-to: type=gha,mode=max
# Sign the resulting Docker image digest except on PRs.
# This will only write to the public Rekor transparency log when the Docker
# repository is public to avoid leaking data. If you would like to publish
# transparency data even for private images, pass --force to cosign below.
# https://github.com/sigstore/cosign
- name: Sign the published Docker image
if: ${{ github.event_name != 'pull_request' }}
env:
# https://docs.github.com/en/actions/security-guides/security-hardening-for-github-actions#using-an-intermediate-environment-variable
TAGS: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.tags }}
DIGEST: ${{ steps.build-and-push.outputs.digest }}
# This step uses the identity token to provision an ephemeral certificate
# against the sigstore community Fulcio instance.
run: echo "${TAGS}" | xargs -I {} cosign sign --yes {}@${DIGEST}
Key areas to note
Events
The events in the above workflow are defined in the on section:
on:
push:
branches: [ "main" ]
# Publish semver (semantic versioning) tags as releases.
tags: [ 'v*.*.*' ]
pull_request:
branches: [ "main" ]
When there is a push on the main branch or a pull request is made on the main branch
Actions
The actions in the above workflow are defined in the jobs.build.steps section:
jobs:
build:
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Install cosign
if: github.event_name != 'pull_request'
uses: sigstore/cosign-installer@59acb6260d9c0ba8f4a2f9d9b48431a222b68e20 #v3.5.0
with:
cosign-release: 'v2.2.4'
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@f95db51fddba0c2d1ec667646a06c2ce06100226 # v3.0.0
- name: Log into registry ${{ env.REGISTRY }}
if: github.event_name != 'pull_request'
uses: docker/login-action@343f7c4344506bcbf9b4de18042ae17996df046d # v3.0.0
with:
registry: ${{ env.REGISTRY }}
username: ${{ github.actor }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
- name: Extract Docker metadata
id: meta
uses: docker/metadata-action@96383f45573cb7f253c731d3b3ab81c87ef81934 # v5.0.0
with:
images: ${{ env.REGISTRY }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}
- name: Build and push Docker image
id: build-and-push
uses: docker/build-push-action@0565240e2d4ab88bba5387d719585280857ece09 # v5.0.0
with:
context: .
push: ${{ github.event_name != 'pull_request' }}
tags: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.tags }}
labels: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.labels }}
cache-from: type=gha
cache-to: type=gha,mode=max
- name: Sign the published Docker image
if: ${{ github.event_name != 'pull_request' }}
env:
TAGS: ${{ steps.meta.outputs.tags }}
DIGEST: ${{ steps.build-and-push.outputs.digest }}
run: echo "${TAGS}" | xargs -I {} cosign sign --yes {}@${DIGEST}
There are seven steps namely:
- Checkout repository - Reads the code in the repository.
- Install cosign - Cosign is a tool that authenticates your container in the registry.
- Setup Docker Buildx - Docker buildx will build your container from code and push it to the container registry.
- Log into a container registry - Log in to your preferred container registry.
- Extract Docker metadata - Extract information related to the docker image.
- Build and push Docker image - Done using the buildx tool installed earlier.
- Sign the published Docker image = Done using cosign setup earlier.
This setup ensures that once you push your code onto github, the container is built and packaged for the container registry.
Connecting to Kubernetes
With the CI/CD connecting our code to our container in the container registry, it is important to note that changes in the container image do not reflect automatically on the pods or deployment. Since it is easier to rollout changes to a deployment rather than a pod, it is better to use that in our CI/CD pipeline
Approach
- Create the docker secret for the container registry
- Create the relevant deployments
- Add the secret for the container registry
- Add the necessary env variables
- Rollout the deployments on changes made
To create a docker secret for the ghcr.io container registry, run the below command:
kubectl create secret docker-registry ghcr-secret --docker-server=ghcr.io --docker-username=<YOUR-USERNAME> --docker-password=<YOUR-GITHUB-PERSONAL-ACCESS-TOKEN>--docker-email=<YOUR-EMAIL>--dry-run=client -o yaml > ghcr-registry-key.yaml
and then apply the file:
kubectl apply -f ghcr-registry-key.yaml
Create the relevant deployments as below:
wazijobs-frontend-deploy.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: wazijobs-frontend
name: wazijobs-frontend
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: wazijobs-frontend
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: wazijobs-frontend
spec:
imagePullSecrets:
- name: ghcr-secret
containers:
- image: ghcr.io/raphaelndonga/wazijobs-frontend:main
name: wazijobs-frontend
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
env:
- name: NEXT_PUBLIC_API_URL_PROD
value: "http://wazijobs-backend-svc"
status: {}
wazijobs-backend-deploy.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: wazijobs-backend
name: wazijobs-backend
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: wazijobs-backend
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: wazijobs-backend
spec:
imagePullSecrets:
- name: ghcr-secret
containers:
- image: ghcr.io/raphaelndonga/wazijobs-backend:main
name: wazijobs-backend
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
## Add the env variables here
env:
- name: PORT
value: "8000"
- name: jwt_key
value: "smartjobsolutions"
- name: DATABASE_URL
value: ""
status: {}
run:
kubectl apply -f wazijobs-frontend-deploy.yaml
kubectl apply -f wazijobs-backend-deploy.yaml
Upon further changes, you can rollout your deployments as below:
kubectl rollout restart deploy wazijobs-frontend
kubectl rollout restart deploy wazijobs-backend
Conclusion
There you have it. Your CI/CD pipeline implemented on Kubernetes through a CI/CD pipeline by Github Actions